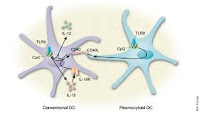
CpG DNA
DNA - CpG islands. In pattedyr genom the bases cytosine (C) would normally be methylated in the 5-position if it occurs in front of the guanine (G). By deamination, which is a spontaneous process that takes place at any time, the methylated C is converted to thymine (T), which is a normal constituent of DNA. This is a mutation that cell's repair systems are difficult to repair and which therefore constitute the most common point mutation in pattedyr genom. Over millions of years have led to the CG sequence or CpG is less frequent in pattedyr genom than might be expected from statistical considerations.
In certain areas of the genome, usually close to the functional genes, C is not methylated in the CpG sequence. The lack of methylation is considered to be one of the mechanisms that regulate the reading of genes. Deamination of C gives the base uracil, which is not a natural constituent of DNA. The cell has developed repair systems which efficiently repair this damage. In non-methylated DNA regions are found not to such an extent that the under representation of CpG that exist in the rest of the genome. These areas therefore called CpG islands or methyl ring-free islands. Since CpG islands usually located near genes, have CpG islands played an important role as tools for localization of genes in the human genome project.